Abstract
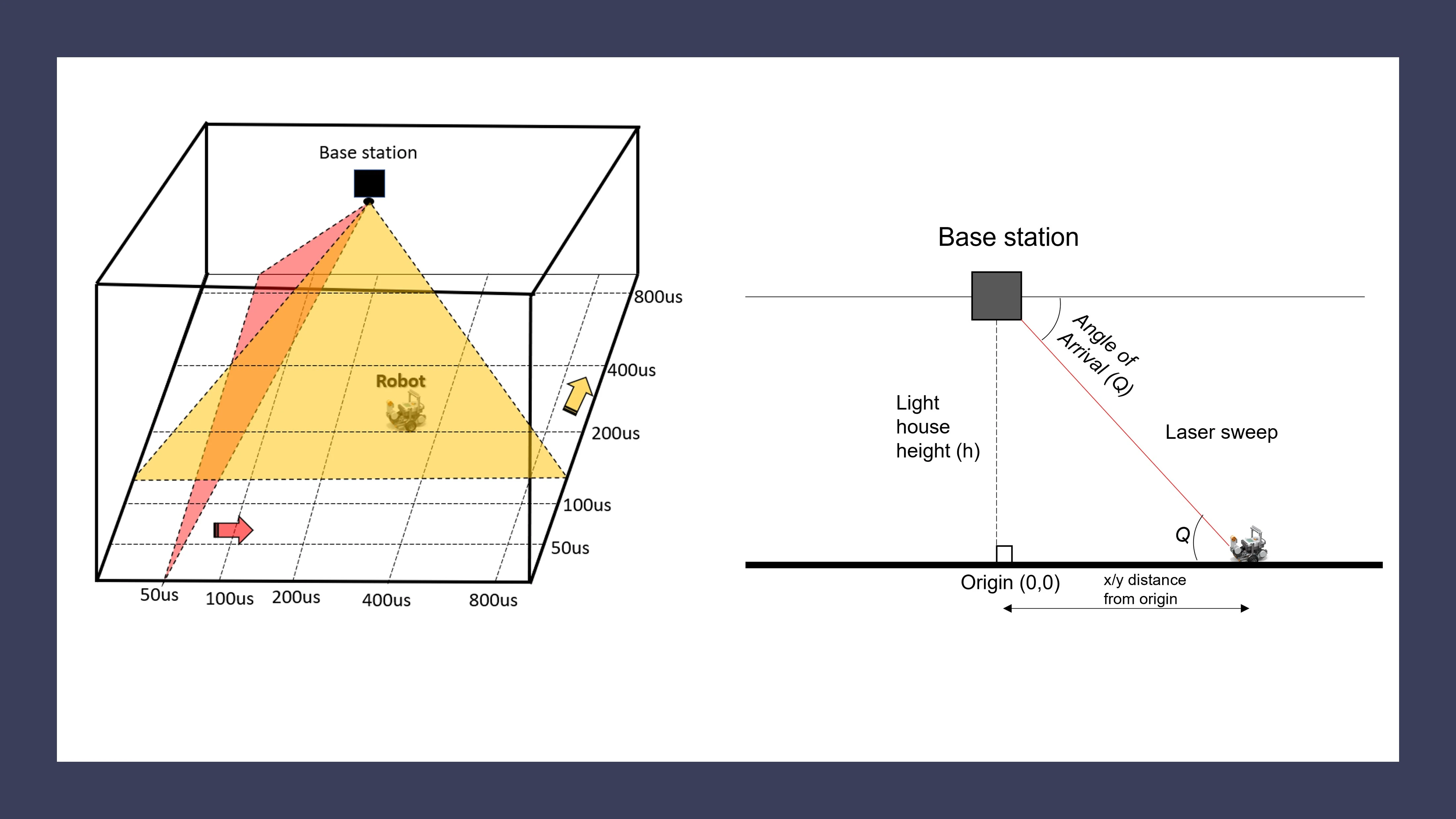
Recent advancements in virtual reality technology have brought us affordable consumer VR devices. One such system is the HTC Vive lighthouse. The lighthouse system was initially developed as a tracking technology for virtual reality gaming applications.
Due to its attractive use-cases in robotics, it is gaining attention as an off-the-shelf tracking system for collecting ground truth position data. It offers a wide field-of-view, high-resolution head-mounted display, and
a room-scale tracking system for an affordable price.
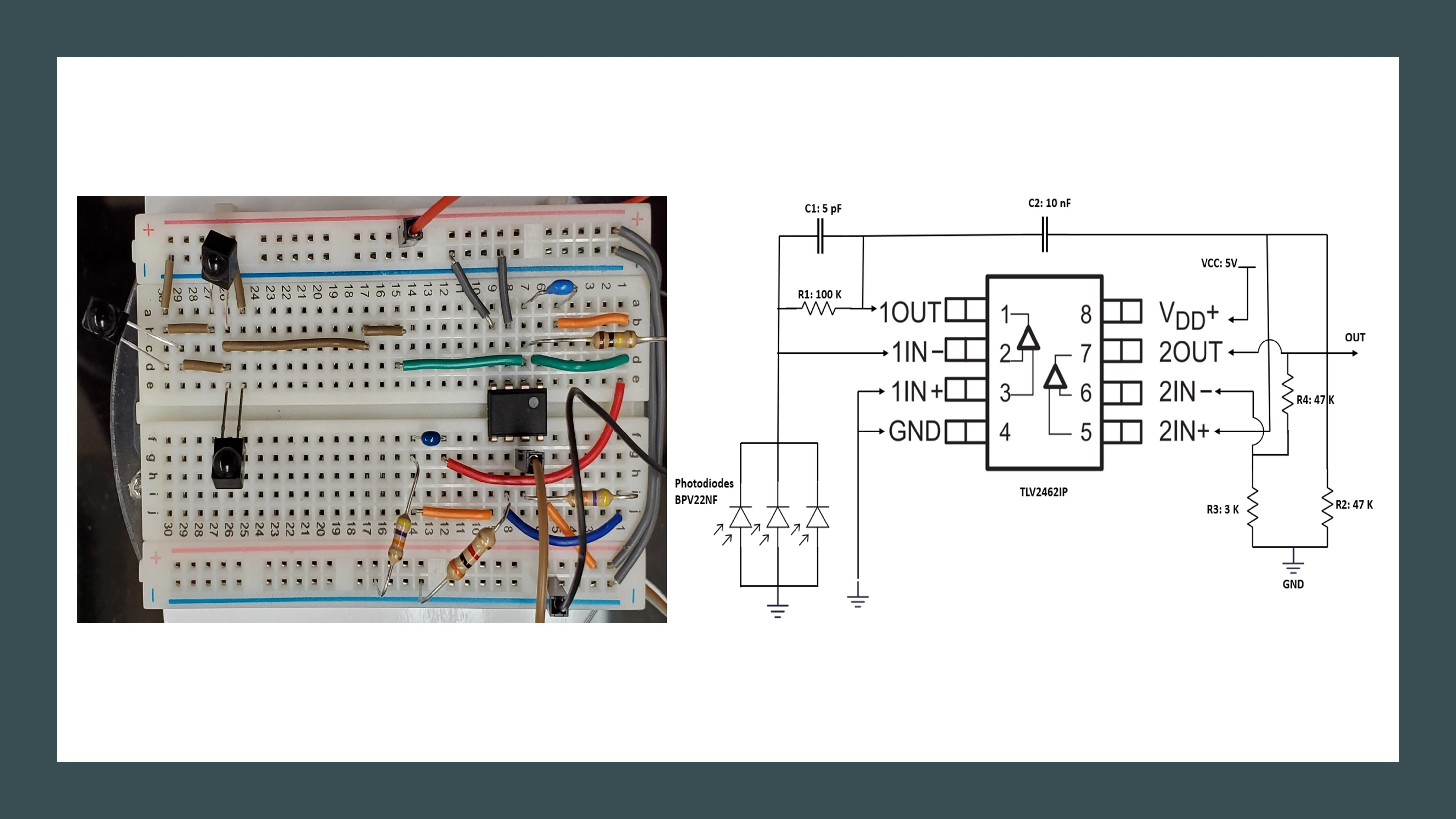
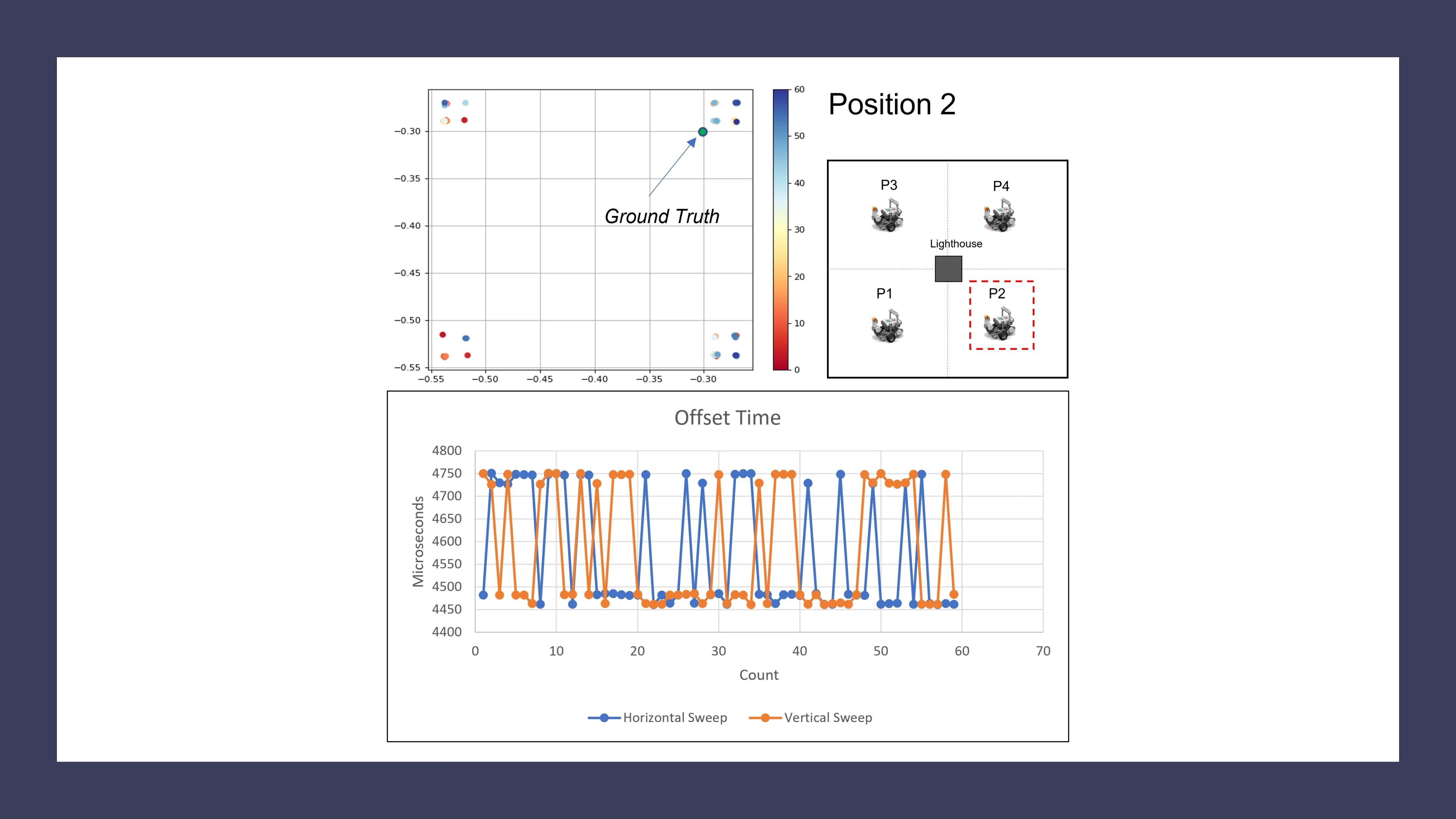
Indoor localization is one of the critical challenges in autonomous robotics. There are many ways to achieve localization, and each has it is pros and cons. Various studies show that HTC Vive could provide precision in millimeter magnitude and accuracy
ranging from 3 to 10 millimeters. Therefore, we intended to study the lighthouse’s functionality and see the possibility of applying it for indoor localization to implement a faster and better solution. Our research studies
and results conclude that the HTC Vive lighthouse positioning system could be a reliable solution for indoor robot localization. With further development, we could more improve the pose estimation accuracy.